Report
Young People and Gambling 2023: Official statistics
Gambling Commission report produced by Ipsos on young people and their gambling behaviour, attitudes and awareness in 2023.
Contents
- Executive summary
- Young people’s active involvement in gambling
- Experience of gambling
- The Impact of gambling on young people
- Online gambling
- National Lottery play
- Games and gaming machines
- The Context for gambling participation
- Attitudes towards and exposure to gambling
-
- Summary
- Young people's views on gambling
- Feeling informed about gambling
- Being stopped from gambling
- Young people's exposure to gambling adverts and promotions and frequency of exposure
- Content of gambling adverts and promotions seen
- Whether ever prompted to gamble by adverts and promotions
- Following gambling companies on social media
- Appendices
- List of gambling activities and definitions
Prevalence of non-problem, at risk or problem gambling
The survey identified 0.7 percent of 11 to 17 year olds as problem gamblers, 1.5 percent as at risk gamblers and 23 percent as non-problem gamblers. Around three quarters (74.2 percent) of young people did not actively gamble in the last 12 months. All data is based on self-reported active involvement in gambling in the last 12 months.
These categories are defined by the problem gambling screen Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th Edition – Multiple Response Juvenile (DSM-IV-MR-J) devised by Fisher (2000). It is important to bear in mind that this is a youth-adapted problem gambler screen, which takes account of adolescent behaviour such as spending dinner money on gambling or arguing with friends. It is not comparable with adult problem gambling screens, which include measures such as the impact of gambling on household finances. Information on how the screen is applied for this survey can be found in the Appendices.
The proportion of young people identified as at-risk gamblers has decreased from 2.4 percent at risk, as has the proportion identified as non-problem gamblers from 27.3 percent, since 2022. The proportion of those who did not actively gamble is now three quarters, 74 percent, having increased 5.5 percentage points.
Figure 2: Types of gambler defined by the youth-adapted problem gambling screen – prevalence of non-problem, at risk or problem gambling
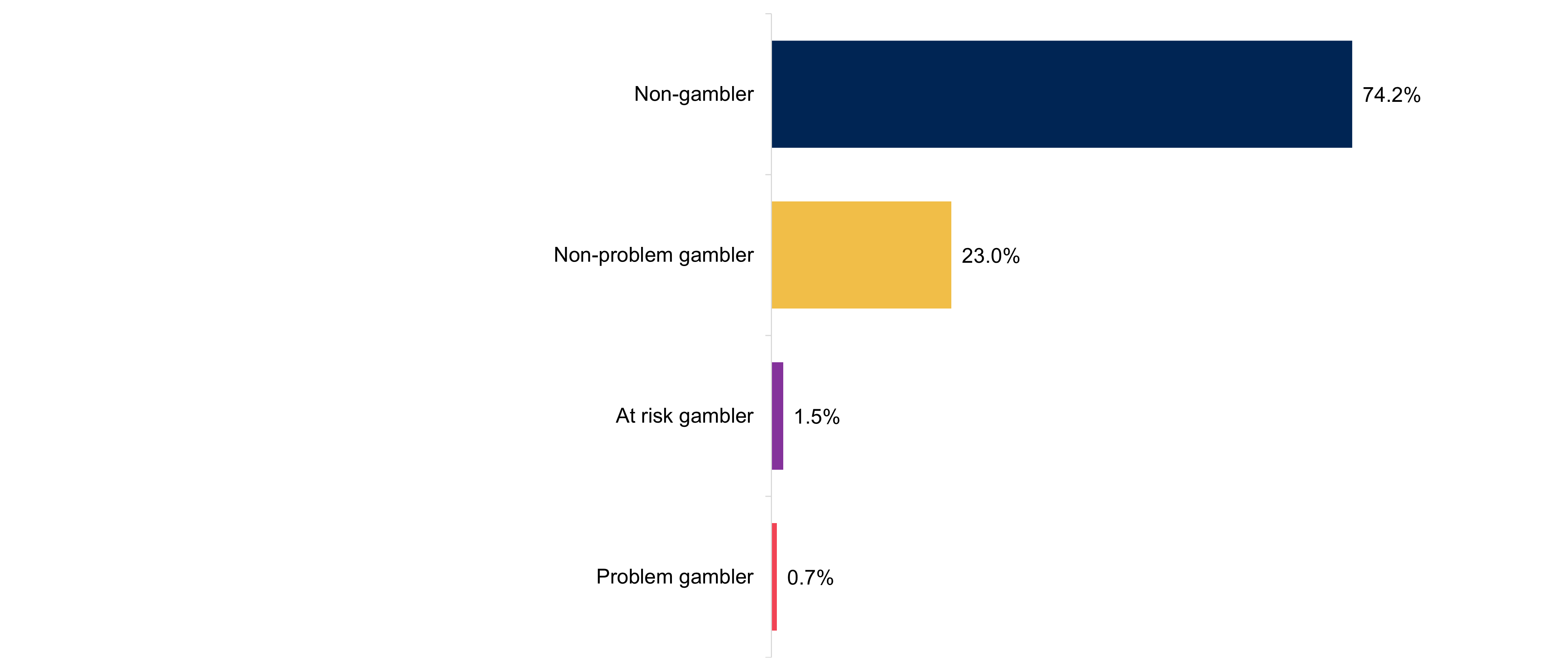
Figure 2 information
Chart shows types of gamblers as defined by the DSM-IV-MR-J youth-adapted problem gambling screen.
Base: All 11 to 17 year olds answering (3,453).
Note: The chart does not show the 1 percent of gamblers who did not provide a response at any question in the gambling screen.
| Types of gamblers | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Non-gambler | 74.2% |
| Non-problem gambler | 23.0% |
| At risk gambler | 1.5% |
| Problem gambler | 0.7% |
Variations in active involvement in types of gambling activities Next section
Problem gambling by gender
Last updated: 7 November 2025
Show updates to this content
Non-gambler figure corrected.
